eXtensions - Friday 25 July 2025
By Graham K. Rogers
![]()
Ever since wearable devices became practical, health care and the proper use of recorded data has been important. This informs the user of the current situation, while analysis of data collected over time allows a picture to be created of the person's general health. It can also be used to make accurate predictions. A group of Year 3 Electrical Engineering Students at Mahidol University, in Thailand, won a contest with an idea for analysis of heart signal patterns to detect ischemic conditions in real time.
As people age, so the blood vessels in the body change, causing problems and worsening health. Hardening and other changes may cause varicose veins (Mayo Clinic). Older people may also suffer from Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). If blood vessels become restricted or blocked, this may cause ischemia: a lack of oxygen [in the blood]. Among other problems, this may cause heart attack or stroke (WebMD).
A group of Year 3 students from the Department of Electrical Engineering of Mahidol's Faculty of Engineering, developed a solution that could help heart patients by analyzing heart-signal patterns to detect ischemic conditions in real time using portable ECG devices and artificial intelligence. An electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) is a diagnostic tool that records [the] heart's electrical activity (Cleveland Clinic). As reported by Columbia University this AI approach is seeing wide acceptance for several aspects of heart health. Team ECG had three members:
The project advisor was Assistant Professor Aranee Pangarad PhD, who specializes in medical imaging, and who has brought many new ideas to teaching students at the Faculty.

|

|

|
The students presented their project at the METI School: AI Biznovation Hackathon, organized by the Mahidol University Faculty of Graduate Studies, in collaboration with Amazon Web Services (AWS). Student teams were tasked to develop AI-driven business solutions. Eight teams who demonstrated how AI can transform industry and address social needs took part in the final event.
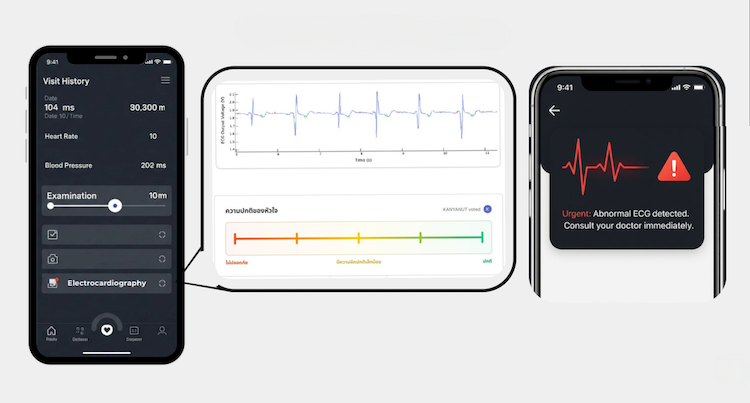
Team ECG explained that the system uses a portable 3-lead ECG device connected to a cloud-based platform. The ECG signal is sent to the cloud, and the AI model analyzes the signal. It sends alerts if abnormalities are detected. All data is securely stored using AWS cloud services. The system provides dashboards and APIs for healthcare providers to track trends, mitigate risks, allowing prompt intervention.
The students hope that the project will reduce preventable cardiac deaths. It also empowers insurance providers to proactively manage risks, reducing the burden of late-stage claims. They would also like to see such innovations transform Thailand's healthcare system by leveraging digital health technologies.
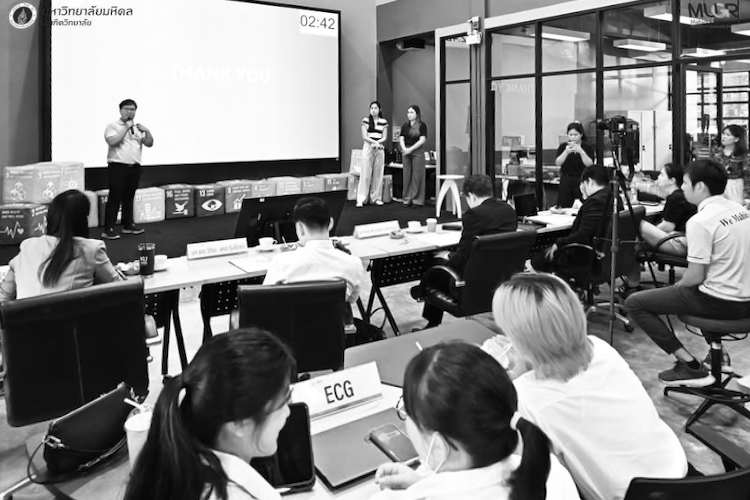

As part of the contest, each group had to come up with a business plan. The group decided on a B2B2C model, working with insurance companies and indirectly reach end users. The business design, included a portable 3-lead ECG device bundled with a real-time AI analysis service. Each bundle would be priced at 6,900 THB with an integrated cloud platform that helps detect signs of cardiac issues. That cloud-based infrastructure would allow scalability to support users across the country. The design of the project would also follow medical data encryption standards.
With this plan they expected to break even at 102 devices with a net profit margin of 39.85% and 50% ROI within the first year. For the long term, they planned an expansion to clinics, pharmacies, and elderly care centers, and intended to explore opportunities for partnerships with the health sector. The judges of the event praised the technical abilities and the commercial potential of their solution: ECG As A Service. They awarded the team a cash prize of ฿50,000.
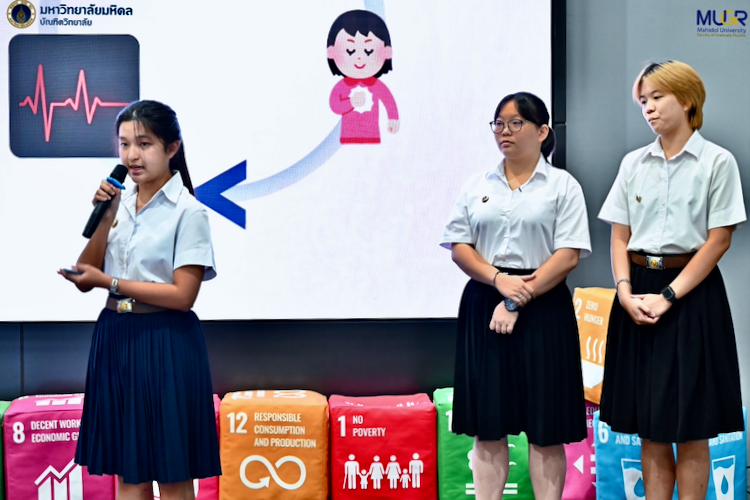

The METI School Hackathon is a demonstration of the commitment to innovative ideas that benefit business and society that Mahidol University encourages in its students as part of an emphasis on innovation, particularly in healthcare. The success of Team ECG demonstrates the academic excellence of the students and the way the University supports future generations of student entrepreneurs.
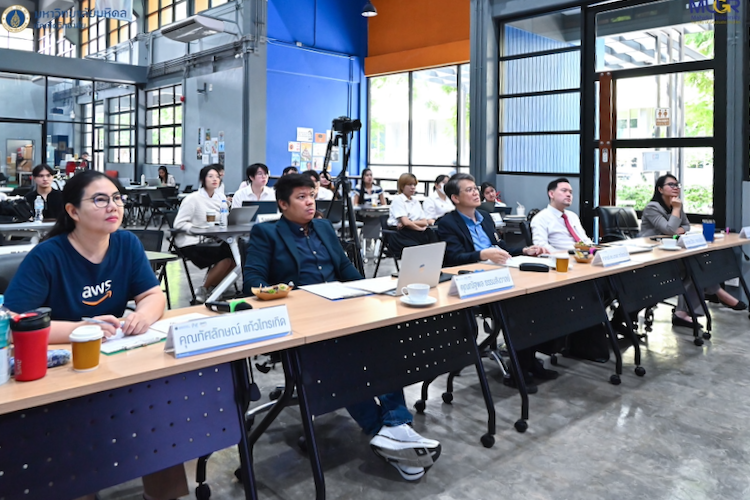

See also: Detecting structural heart disease from electrocardiograms using AI (Nature).
Graham K. Rogers teaches at the Faculty of Engineering, Mahidol University in Thailand. He wrote in the Bangkok Post, Database supplement on IT subjects. For the last seven years of Database he wrote a column on Apple and Macs. After 3 years writing a column in the Life supplement, he is now no longer associated with the Bangkok Post. He can be followed on X (@extensions_th). The RSS feed for the articles is http://www.extensions.in.th/ext_link.xml - copy and paste into your feed reader.

For further information, e-mail to
Back to
eXtensions
Back to
Home Page